LED Light Emission: How It Works and What You Need to Know
Light-emitting diodes, commonly known as LEDs, have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. LEDs are a type of solid-state lighting that emits light when electric current passes through a semiconductor material. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, which generate light by heating a filament, LEDs convert electrical energy into light, making them more efficient and cost-effective. LEDs are now used in a wide range of applications, from lighting homes and businesses to illuminating stadiums and landmarks. With the growing popularity of LEDs, it’s important to understand how they work and what factors affect their performance. In this article, we will explore the science behind LED light emission and discuss the key factors to consider when choosing LED lighting solutions. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to upgrade your lighting or a business owner looking to improve energy efficiency, understanding the basics of LED technology can help you make informed decisions and choose the best lighting solutions for your needs.
LED lights, or light-emitting diodes, are a type of energy-efficient lighting that has become increasingly popular in recent years. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, which use a filament to produce light, LEDs use a semiconductor to convert electrical energy into light. LED lights are highly efficient, consuming much less energy than traditional bulbs while still producing bright, high-quality light. They are also highly durable, with a lifespan of up to 50,000 hours, which can greatly reduce the need for maintenance and replacement over time. Additionally, LED lights come in a wide range of colors and styles, making them a versatile and attractive option for a variety of lighting needs.
LED lights have revolutionized the way we light up our world. With their low energy consumption, long lifespan, and high efficiency, they have become an indispensable part of modern life. LED lights are used in everything from streetlights to smartphones, and they have replaced traditional incandescent bulbs in homes and businesses. They emit a bright white light that is easy on the eyes and can be customized to create different colors and effects. LED lights are also environmentally friendly, as they produce less heat and contain no toxic materials. Thanks to LED technology, we can enjoy brighter, more energy-efficient lighting that lasts longer and is better for the planet.
How LED Light Emission Works

Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are one of the most efficient and energy-saving forms of lighting technology available today. But how do they work? In short, LED light emission is the result of a process called electroluminescence. This is a phenomenon in which a material emits light in response to an electrical current. In the case of LEDs, electroluminescence occurs in a semiconductor material that has been doped, or impregnated, with impurities to create a p-n junction. When a voltage is applied to the p-n junction, electrons and holes recombine, releasing energy in the form of photons. This generates the visible light that we see. One of the key advantages of LED light emission is that it is highly directional. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which emit light in all directions, LEDs can be designed to emit light in a specific direction. This is because the photons emitted by an LED are confined to a narrow beam, thanks to the design of the p-n junction. Additionally, LED light emission is very efficient, with up to 90% of the energy consumed by an LED being converted into light. This makes LEDs an excellent choice for applications in which energy efficiency and directional illumination are important, such as in automotive lighting, traffic signals, and backlighting for displays.
Semiconductors are materials that have an electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. They are made up of atoms with incomplete outer shells, which can move around and leave behind \holes\ that can be filled by electrons. The movement of electrons and holes within a semiconductor material is critical to the operation of LED lights. When a voltage is applied to the semiconductor material, electrons are pushed from the negative electrode towards the positive electrode, while holes are pushed in the opposite direction. As they move towards each other, electrons fall into holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. This process is known as recombination, and it is what causes the emission of light in LEDs. By controlling the composition and doping of the semiconductor material, engineers can tailor the properties of the LED to emit different colors of light.
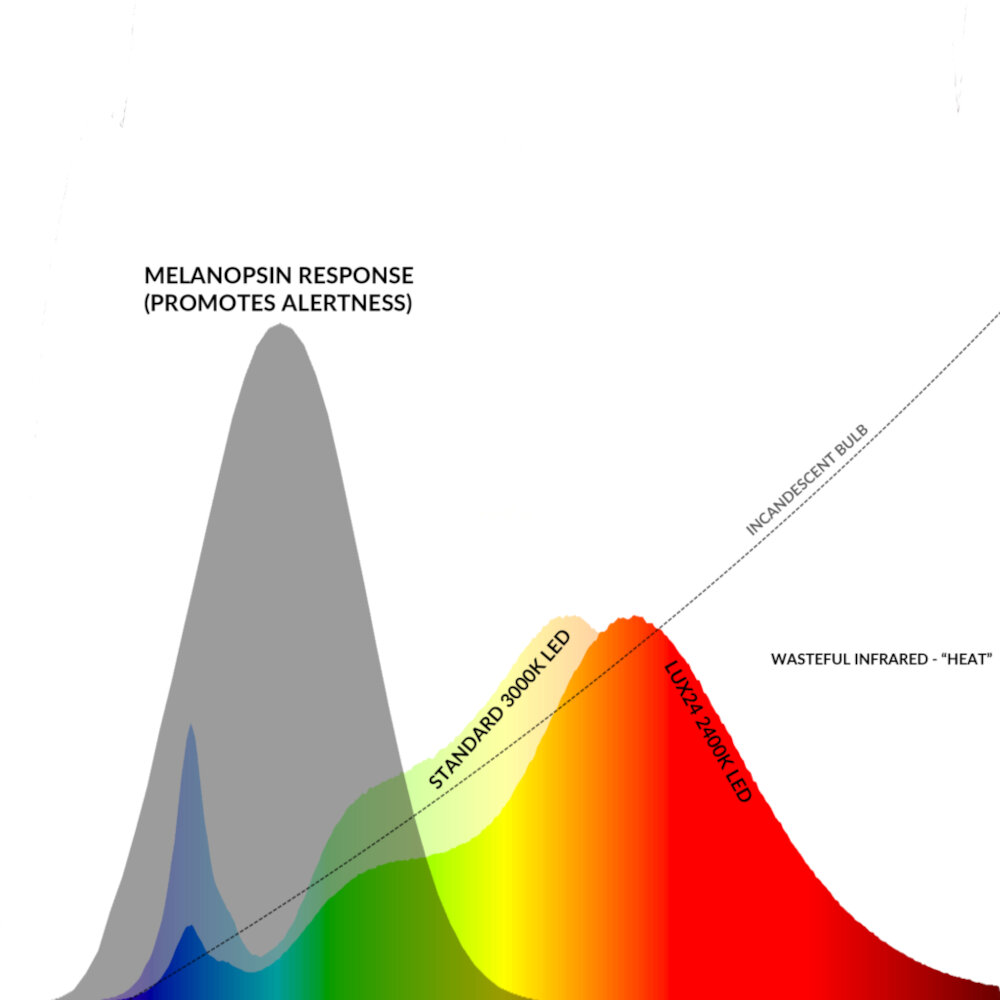
Electron movement is the fundamental principle behind LED light emission, which occurs when electrons move from a higher energy level to a lower energy level. The movement of electrons is facilitated by the presence of a semi-conductor material, which acts as a pathway for the electrons to flow through. As the electrons move, they release energy in the form of photons, which are packets of light energy. The color of the light emitted is determined by the amount of energy released, with higher energy levels producing shorter wavelengths and therefore bluer light. This process is highly efficient, with very little energy being lost as heat, making LEDs a popular choice for lighting applications.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. There are different types of LED lights, including organic LEDs (OLEDs), traditional LEDs, and high-power LEDs. OLEDs are made of thin layers of organic materials and emit light when an electric current passes through them. Traditional LEDs are made of a semiconductor material, such as gallium arsenide, and emit light when an electric current is passed through a junction in the material. High-power LEDs are similar to traditional LEDs but can handle higher levels of current and produce more light. These LEDs emit light through a process called electroluminescence, where an electric current excites electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to emit photons.
Factors Affecting LED Light Emission

LED (Light Emitting Diode) has revolutionized the lighting industry with its energy efficiency and long-lasting performance. However, the light emission of an LED is affected by various factors that need to be considered for optimal performance. One of the most critical factors is the material used in the construction of LED. The material dictates the color of the LED light, and the most commonly used materials are gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, and aluminum gallium arsenide. The composition of these materials affects the amount of energy required for light emission and the intensity of the light produced. Additionally, the size of the LED chip also impacts the light emission as smaller chips produce less light than larger chips. Another important factor affecting LED light emission is the operating temperature. LED light output decreases as the temperature increases, due to the increased resistance of the semiconductor material. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the thermal design of the LED system to ensure optimal performance. The thermal design should include proper heat sinking and ventilation to dissipate the heat generated by the LED efficiently. Furthermore, the current supplied to the LED also affects light emission as higher current leads to higher light output but also increases the operating temperature. Hence, it is essential to find the right balance between current and temperature to achieve the desired light output and maintain the LED’s longevity.
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and lifespan of LED lights. These lights generate heat as a byproduct of their energy-efficient operation. If the temperature of the LED light exceeds its maximum operating temperature, the light output may decrease, and the lifespan may be significantly reduced. Therefore, efficient heat management is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of LED lights. This is typically achieved through the use of heat sinks, which dissipate heat away from the LED diode and into the surrounding environment. Additionally, LED lights are designed to operate at specific temperatures, which are typically listed in the manufacturer’s specifications. By adhering to these temperature guidelines, you can ensure that your LED lights perform optimally and have a long lifespan.
LED light emission is a fascinating phenomenon that involves the flow of current and voltage. Current refers to the flow of electric charge, which is measured in amperes (A). In LED lighting, the current passes through a semiconductor material, which emits light when the electrons recombine with the holes. Voltage, on the other hand, is the measure of the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, and it is measured in volts (V). In LED lighting, the voltage is applied to the p-n junction of the semiconductor material, which causes the electrons to flow and emit photons. Understanding the relationship between current and voltage is essential in the design and operation of LED lighting systems, as it affects the brightness, color, and efficiency of the light emitted.
Material quality plays a crucial role in determining the performance and efficiency of LED light emission. The quality of the semiconductor material used in the LED chip directly affects its ability to emit light. High-quality semiconductors with a high purity level and minimal defects allow for efficient electron flow and better light production. In addition, the quality of the substrate and the bonding process used in the manufacturing of LED chips can also affect the overall performance of the LED. Poor quality materials or manufacturing processes can lead to lower efficiency, shorter lifespan, and inconsistent light output. Therefore, it is essential to ensure the use of high-quality materials in the production of LED chips to achieve optimal performance and longevity.
External factors such as humidity and dust can have a significant impact on the performance of LED lights. High humidity levels can cause condensation to form on the surface of the LED, which can lead to corrosion and reduced light output. Dust can also accumulate on the surface of the LED, which can block the light and reduce its effectiveness. In addition, dust can also cause overheating of the LED, which can damage the internal components and reduce its lifespan. To ensure proper functioning of LED lights, it is important to consider these external factors and take appropriate measures to protect the LED from these elements.
Applications of LED Light Emission

LED light emission has revolutionized the lighting industry due to its energy efficiency and long lifespan. LEDs are used in various applications, from household lighting to automotive lighting and even in medical equipment. One of the most common uses of LED lighting is in televisions and computer screens. LED backlights provide bright and crisp images while consuming less power than traditional LCD screens. In addition, LEDs are used in the automotive industry for headlights, brake lights, and turn signals. LED lights are brighter, have a longer lifespan, and consume less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. This makes them an excellent choice for automotive lighting, where durability and energy efficiency are essential. Another application of LED lighting is in horticulture. LED grow lights provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth and are more efficient than traditional fluorescent and HID lights. LED grow lights have a longer lifespan and consume less energy, allowing farmers and gardeners to save on electricity costs while producing healthier and more abundant crops. Additionally, LED lighting is used in medical equipment such as surgical lights, phototherapy devices, and dental curing lights. LED medical lighting provides brighter and more focused light while consuming less power than traditional halogen lamps. This makes them an ideal choice for medical professionals who need precise and high-quality lighting for their work. Overall, the applications of LED light emission are vast and varied, and they are sure to continue expanding as technology advances.
The lighting industry has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, with the introduction of LED technology. LEDs have revolutionized the way we think about lighting, offering improved energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and a wider range of color options compared to traditional lighting sources. The basic principle behind LED light emission involves the transfer of electrons between different materials, resulting in the release of energy in the form of light. This process, known as electroluminescence, is what makes LED lights so efficient and versatile. Whether you’re looking to brighten up your home or improve the lighting in your workplace, LED technology has a lot to offer.
The automotive industry is a rapidly evolving sector that is constantly incorporating new technologies to improve vehicle performance, safety, and efficiency. One such technology that has gained popularity in recent years is LED lighting. LED lights offer a range of benefits over traditional halogen bulbs, including longer lifespan, lower power consumption, and brighter and more focused illumination. LED lights can be used for headlights, taillights, brake lights, and interior lighting, and are also popular in aftermarket modifications. As the demand for energy-efficient and high-performance lighting solutions continues to grow, the automotive industry is likely to see further innovation and development in the field of LED lighting.
Consumer electronics have revolutionized the way we live our lives. From smartphones to smart TVs, these devices have made our lives easier and more connected than ever before. One of the most important consumer electronics is LED lights. LED lights are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and offer a wide range of colors and brightness levels. They work by converting electricity into light through a process called electroluminescence. This process produces light when electrons move through a semiconductor material. LED lights have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their energy efficiency and versatility. They are used in a variety of applications, including residential lighting, commercial lighting, and automotive lighting.
The medical field has been revolutionized by the introduction of LED light emission technology. LED lights have been used in a variety of medical applications, including surgical lighting, phototherapy, and wound healing. The benefits of LED light include energy efficiency, long lifespan, and the ability to produce a variety of colors. In surgical settings, LED lighting can provide bright, high-quality illumination without generating excessive heat, which is essential for the comfort of both the patient and the surgical team. Additionally, LED light therapy has shown promising results in treating a variety of medical conditions, including skin disorders, pain management, and depression. Overall, LED light technology has become an essential tool in the medical field, providing high-quality lighting and therapeutic benefits that improve patient outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LED Light Emission

LED light emission has revolutionized the lighting industry and is considered one of the most energy-efficient and cost-effective lighting options available. LED lights offer several advantages over traditional lighting sources, including longer lifespan, low energy consumption, and high brightness. LED lights are also known for their durability and reliability, making them ideal for use in a variety of applications. LED lights also have some disadvantages that should be taken into consideration. One of the biggest disadvantages of LED lights is their higher initial cost compared to traditional lighting sources. However, this cost is offset by the energy savings and longer lifespan of LED lights. Another disadvantage of LED lights is their sensitivity to temperature changes, which can affect their performance. Additionally, LED lights can produce a bluish-white light that may not be suitable for certain applications, although newer LED technologies have improved the color rendering capabilities of LED lights.
When it comes to lighting, energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness are two crucial factors to consider. Traditional incandescent bulbs are notoriously inefficient, wasting up to 90% of their energy as heat. On the other hand, LED light emission is much more efficient, converting up to 80% of its energy into light. This not only saves on energy costs but also reduces the strain on the environment. Additionally, while LED bulbs may cost more upfront than traditional bulbs, their longer lifespan and energy efficiency make them a cost-effective choice in the long run. When selecting lighting for your home or business, it’s important to consider both the upfront cost and the long-term savings that come with energy-efficient options like LED lighting.
One of the most significant advantages of LED light emission is its long lifespan and durability. LED lights can last up to 50,000 hours or more, making them a cost-effective lighting solution in the long run. Unlike traditional light bulbs that burn out and need frequent replacements, LEDs are designed to maintain their brightness and functionality over time. Additionally, LED lights are highly resistant to shock, vibrations, and temperature changes, making them ideal for use in harsh environments. This durability also means less maintenance, fewer replacements, and less waste, making LEDs a sustainable and eco-friendly lighting option.
Limited color options are one of the main drawbacks of LED lights. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that emit a warm, yellowish light, LED bulbs are capable of producing a wide range of colors. However, not all LED bulbs are created equal. Some LED bulbs are designed to emit only a narrow range of colors, while others are capable of producing a wider range of colors. This limitation can be particularly frustrating for individuals who are looking to create a certain ambiance or mood in their interior spaces. However, recent advances in LED technology have led to the development of bulbs that are capable of producing a wider range of colors, which should help to alleviate this issue in the future.
When it comes to LED light emission, one of the primary concerns that people have is the initial investment cost. While it is true that LED lights can be more expensive than traditional lighting options, it is important to consider the long-term savings that they can provide. LED lights have a longer lifespan than traditional bulbs, which means that you will not have to replace them as frequently. Additionally, LED lights are more energy-efficient, which can result in lower electricity bills over time. When you take these factors into account, the initial investment cost of LED lights may be well worth it in the end.
LED light emission is a fascinating process that occurs when an electric current passes through a semiconductor material, which then releases energy in the form of light. This process is known as electroluminescence and is an efficient way of generating light. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LED bulbs do not rely on the heating of a filament to create light, making them much more energy-efficient and longer-lasting. LED lights are becoming increasingly popular due to their low energy consumption, durability, and versatility. They are used in a variety of applications, including lighting in homes, commercial buildings, automobiles, and even in horticulture to grow plants. Understanding the LED light emission process is essential to ensure that we use this technology in the most effective way possible, reducing our carbon footprint and contributing to a more sustainable future.
The future of LED technology is bright, both in terms of energy efficiency and innovative applications. Advancements in LED manufacturing techniques are leading to more efficient and longer-lasting bulbs, while research into new materials is expanding the spectrum of colors available. Additionally, the ability to control LED lighting with smart technology is creating new avenues for customization and energy management. With the growing demand for sustainable and cost-effective lighting solutions, it is likely that LED technology will continue to evolve and improve in the years to come, making it an exciting field to watch.
Conclusion

In conclusion, LED light emission is a fascinating and innovative technology that has revolutionized the lighting industry. By understanding how it works, you can appreciate the benefits it offers, such as energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and lower maintenance costs. Whether you are a homeowner, business owner, or lighting professional, knowing what you need to know about LED lighting can help you make informed decisions and choose the right LED products for your needs. So, embrace this technology and enjoy the many benefits it offers for years to come!